If you have a persistent earache or a scratchy throat that seems out of proportion to a mild cold, you may wonder, can wisdom teeth cause ear and throat pain? The answer is yes. Wisdom teeth, or third molars, sit at the back of the mouth and share nerve pathways with the jaw joint, throat and ears. When those common teeth erupt without enough room or become trapped beneath bone, they can trigger other uncomfortable symptoms such as earache, jaw stiffness and throat irritation.
How impacted wisdom teeth send pain to strange places
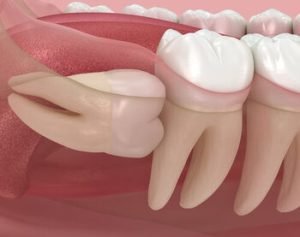
The same mechanism explains why wisdom teeth cause a sore throat. Inflamed, swollen tissue at the back of the mouth lies only millimetres from the pharyngeal wall. When the inflamed infection site enlarges, every swallow can worsen a sore throat.
Typical symptoms that point to your third molars
While referred pain can be confusing, common symptoms around the wisdom tooth area still tend to appear:
- Swollen gums tenderness behind the last permanent teeth
- Localised tooth pain or dull pressure in the lower wisdom teeth
- Red or bleeding gum tissue
- Jaw stiffness and radiating jaw pain
- Unpleasant taste or bad breath when food particles collect under a gum flap
- Limited ability to open the mouth properly
If an infected wisdom tooth is left untreated, the bacterial load can evolve into an abscessed tooth. That abscess may drain toward the throat, compounding irritation. Likewise, untreated tooth decay leads to deeper pulp involvement; untreated tooth decay not only harms the offending molar but eventually leads to infection that spreads along tissue planes.
Why wisdom teeth can cause much more than a local toothache
Because wisdom teeth erupt later than any neighbouring molar, there is often not enough space for them to align. The resulting tooth movement can damage nearby teeth, crowd orthodontic work and trap debris in hard-to-clean pockets. Trapped bacteria thrive, and their toxins inflame the infection site. If oral hygiene is challenging back there, plaque accumulates and tooth decay accelerates. Over time, an infected tooth or pericoronal infection may spread to the jaw bone and the underlying socket, intensifying discomfort.
When infected wisdom teeth discharge pus near the tonsils, those teeth cause a sore tickle that lingers. In severe cases, swelling under the tongue and in the airway can become an emergency.
When infection travels: ear, throat and beyond
Once bacteria breach the soft tissues, they follow the path of least resistance. Lymph nodes enlarge, and pus may track toward the Eustachian tube, explaining why wisdom teeth cause ear fullness. Simultaneously, oedema near the tonsils makes it hard to swallow. Patients can present with typical symptoms, such as fever or trismus, or report recurring sore throats after chewing.
Treatment options: from conservative care to surgery
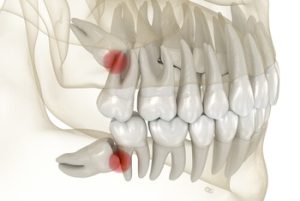
A straightforward wisdom tooth extraction under local anaesthetic removes the source of pressure and halts the bacterial cycle. In many cases, only one impacted wisdom tooth is symptomatic, but dentists will assess all four impacted wisdom teeth because a silent infection can smoulder elsewhere. Extraction eliminates the nidus of disease and allows the gum tissue to heal.
What to expect after surgery
Modern surgical technique protects oral health while minimising downtime. Mild swelling and temporary uncomfortable symptoms, such as stiffness, are normal, but patients typically find that ear and throat irritation resolves within days once the infection site is cleared. Post-operative instructions include gentle brushing of the tooth site, avoiding smoking (which dries the clot in the underlying socket) and a soft-food diet.
Prevention: keep an eye on those third molars

Regular check-ups with your dentist should include evaluation of third-molar status, review of radiographs, and tailored advice on timing for extraction. That professional guidance reduces the risk that wisdom teeth can cause secondary ENT complaints.
Key takeaways
- Wisdom teeth sit close to major nerves; inflamed tissue in that zone easily refers pain to the ears and throat.
- Crowding and partial eruption foster pockets where bacteria breed, creating an infection that may spread to the throat or ears.
- Red flags include recurring ear pain, chronic sore throat on one side, foul taste or visible swollen gums and tenderness behind the molars.
- Definitive management usually means surgical removal; delay can mean other symptoms like facial swelling or spreading cellulitis.
If you’re concerned about earache, throat discomfort, or jaw pain linked to your wisdom teeth, book a consultation or call (08) 7078 8263.
Resources
Duran, R. & Seed, S. (2024). ‘What Is an Abscessed Tooth?’. WebMD, 16 January. New York, NY: WebMD LLC. https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/abscessed-tooth
Cleveland Clinic. (2023). ‘Wisdom Teeth’. Cleveland Clinic, 12 September. Cleveland, OH: Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/23223-wisdom-teeth
Note: Any surgical or invasive procedure carries risks. Before proceeding, you should seek a second opinion from an appropriately qualified health practitioner.

